2 El Presente / The Present Tense (Amo)
El Presente / The Present Tense (Amo)
The Present Tense is used to talk about the here and now, or about things that you do regularly:
I am running.
I run every day.
The following examples show how to conjugate ar, er and ir verbs in the Present Tense.
ar Example:
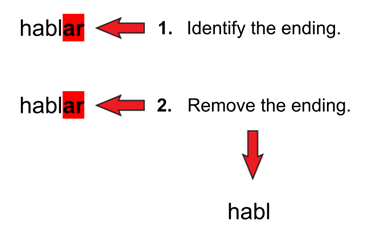
| Step 3 | Yo | hablo |
| Tú | hablas | |
| Él/Ella/Usted | habla | |
| Nosotros/Nosotras | hablamos | |
| Vosotros/Vosotras | habláis | |
| Ellos/Ellas/Ustedes | hablan |
From this, we can see that the endings for ar verbs in the Present Tense are:
o
as
a
amos
áis
an
er Example:
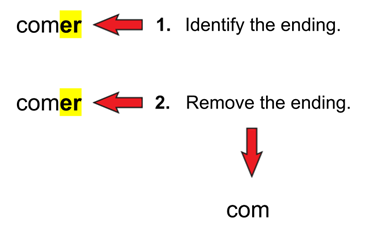
| Step 3 | Yo | como |
| Tú | comes | |
| Él/Ella/Usted | come | |
| Nosotros/Nosotras | comemos | |
| Vosotros/Vosotras | coméis | |
| Ellos/Ellas/Ustedes | comen |
From this, we can see that the endings for er verbs in the Present Tense are:
o
es
e
emos
éis
en
ir Example
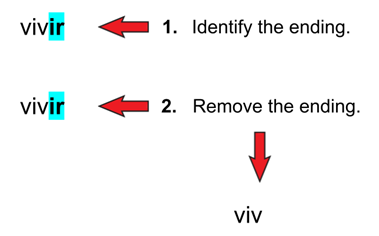
| Step 3 | Yo | vivo |
| Tú | vives | |
| Él/Ella/Usted | vive | |
| Nosotros/Nosotras | vivimos | |
| Vosotros/Vosotras | vivís | |
| Ellos/Ellas/Ustedes | viven |
From this, we can see that the endings for ir verbs in the Present Tense are:
o
es
e
imos
ís
en
Irregular Present Tense Verbs
Not all verbs follow the pattern of just adding ar, er or ir endings. Verbs that follow this pattern are called regular verbs, and verbs that follow different patterns are called irregular verbs. As irregular verbs don’t follow the normal rules, they have to be learned individually.
Estar is an irregular verb which means “to be”. The following table shows estar in the Present Tense.
| Person | Estar | English |
| Yo | estoy | I am |
| Tú | estás | You are |
| Él/Ella/Usted | está | He is, She is, You are |
| Nosotros/Nosotras | estamos | We are |
| Vosotros/Vosotras | estáis | You (all) are |
| Ellos/Ellas/Ustedes | están | They are, You (all) are |
The verb Ser is irregular, and also means “to be”. The following table shows ser in the Present Tense.
| Person | Ser | English |
| Yo | soy | I am |
| Tú | eres | You are |
| Él/Ella/Usted | es | He is, She is, You are |
| Nosotros/Nosotras | somos | We are |
| Vosotros/Vosotras | sois | You (all) are |
| Ellos/Ellas/Ustedes | son | They are, You (all) are |
Ir is an irregular verb meaning “to go”. Although this verb just looks like an ir ending, it is a verb in itself. It is used a lot in Spanish, so make sure to pay special attention to the following table showing its form in the Present Tense.
| Person | Ir | English |
| Yo | voy | I am |
| Tú | vas | You are |
| Él/Ella/Usted | va | He is, She is, You are |
| Nosotros/Nosotras | vamos | We are |
| Vosotros/Vosotras | vais | You (all) are |
| Ellos/Ellas/Ustedes | van | They are, You (all) are |
Here are several more irregular verbs:
| Person | Dar | English |
| Yo | doy | I am |
| Tú | das | You are |
| Él/Ella/Usted | da | He is, She is, You are |
| Nosotros/Nosotras | damos | We are |
| Vosotros/Vosotras | dais | You (all) are |
| Ellos/Ellas/Ustedes | dan | They are, You (all) are |
| Person | Ver | English |
| Yo | veo | I am |
| Tú | ves | You are |
| Él/Ella/Usted | ve | He is, She is, You are |
| Nosotros/Nosotras | vemos | We are |
| Vosotros/Vosotras | veis | You (all) are |
| Ellos/Ellas/Ustedes | ven | They are, You (all) are |
| Person | Oír | English |
| Yo | oigo | I am |
| Tú | oyes | You are |
| Él/Ella/Usted | oye | He is, She is, You are |
| Nosotros/Nosotras | oímos | We are |
| Vosotros/Vosotras | oís | You (all) are |
| Ellos/Ellas/Ustedes | oyen | They are, You (all) are |
The following verbs are irregular in the yo form only (except for tener, venir and decir, which also have other irregularities).
| Verbs that add g before o | ||
| Verb | Yo Form | English |
| hacer | hago | I do |
| poner | pongo | I put |
| salir | salgo | I go out |
| valer | valgo | I am worth |
| traer | traigo | I bring |
| caer | caigo | I fall |
| tener | tengo | I have |
| venir | vengo | I come |
| decir | digo | I come |
| Verb | Yo Form | English |
| saber | sé | I know |
| caber | quepo | I fit |
| Verbs that add z | ||
| Verb | Yo Form | English |
| conocer | conozco | I know |
| ofrecer | ofrezco | I offer |
| merecer | merezco | I deserve |
| aparecer | aparezco | I appear |
| pertenecer | pertenezco | I belong |
| traducir | traduzco | I translate |
| conducir | conduzco | I drive |
| producir | produzco | I produce |
| Verb | Yo Form | English |
| coger | cojo | I catch/take |
| dar | doy | I give |
| ver | veo | I see |
This is not an exhaustive list. There are other verbs that are irregular in the yo form.
Radical Changing Verbs
Radical changing verbs have spelling changes in the last vowel of the stem. This spelling change happens for all forms of the verb in the Present Tense, except for nosotros, nosotras, vosotros and vosotras. There are five groups of radical changing verbs, shown in the tables below.
| e ➡ ie | o ➡ ue | ||||
|
tener
|
venir
|
cerrar
|
dormir
|
encontrar
|
poder
|
| tengo | vengo | cierro | duermo | encuentro | puedo |
| tienes | vienes | cierras | duermes | encuentras | puedes |
| tiene | viene | cierra | duerme | encuentra | puede |
| tenemos | venimos | cerramos | dormimos | encontramos | podemos |
| tenéis | venís | cerráis | dormís | encontráis | podéis |
| tienen | vienen | cierran | duermen | encuentran | pueden |
| u ➡ ue | e ➡ i | i ➡ ie |
|||
| jugar | decir * | pedir | repetir | adquirir | inquirir |
| juego | digo | pido | repito | adquiero | inquiero |
| juegas | dices | pides | repites | adquieres | inquieres |
| juega | dice | pide | repite | adquiere | inquiere |
| jugamos | decimos | pedimos | repetimos | adquirimos | inquirimos |
| jugáis | decís | pedís | repetís | adquerís | inquirís |
| juegan | dicen | piden | repiten | adquieren | inquieren |
Note: * Decir is also irregular in the yo form in the Present Tense (digo).
This is not an exhaustive list. There are many more radical changing verbs in Spanish.
Some verbs have more than one spelling change. This happens so that the pronunciation of the verb doesn’t change when it is conjugated. The following table shows two of these verbs.
|
Person
|
conseguir
|
corregir
|
|
Yo
|
consigo
|
corrijo
|
|
Tú
|
consigues
|
corriges
|
|
Él/Ella/Usted
|
consigue
|
corrige
|
|
Nosotros/Nosotras
|
conseguimos
|
corregimos
|
|
Vosotros/Vosotras
|
conseguís
|
corregís
|
|
Ellos/Ellas/Ustedes
|
consiguen
|
corrigen
|
Los Verbos Reflexivos / Reflexive Verbs (amarse)
Reflexive verbs are made up of two parts: the verb part and the reflexive part. For example, in the verb lavarse (to wash oneself), lavar is the verb part, and se is the reflexive part. Both parts together make up the infinitive of the verb (the infinitive is the verb before we know who does the action or when they do the action).
There are a couple of steps you have to follow to conjugate reflexive verbs.
- Conjugate lavar by itself.
- Move the se from the end of the verb to the front, as a separate word.
- Choose the correct form of se, according to how you conjugated lavar.
The following table shows how to conjugate lavarse in the Present Tense:
|
Personal Pronoun
|
se
|
lavar
|
English
|
|
yo
|
me
|
lavo
|
I wash myself
|
|
tú
|
te
|
lavas
|
You wash yourself
|
|
él
|
se
|
lava
|
He washes himself
|
|
ella
|
se
|
lava
|
She washes herself
|
|
usted
|
se
|
lava
|
You wash yourself (formal)
|
|
nosotros/nosotras
|
nos
|
lavamos
|
We wash ourselves
|
|
vosotros/vosotras
|
os
|
laváis
|
You wash yourselves (plural)
|
|
ellos/ellas
|
se
|
lavan
|
They wash themselves
|
|
ustedes
|
se
|
lavan
|
You wash yourselves (plural, formal)
|
As with all verbs, you don’t have to include the personal pronouns with reflexive verbs.

